Introduction:
A Hydrostatic slide is non-contact in that the slide is supported by a film of high pressure oil, in the order of 10 Um. It functions by producing a continuous flow of high pressure oil through and out of the bearing. The flow rate being controlled by restrictors. The restrictors allow the slideway to cope with varying loads and maintain a near constant film thickness. Throughout the bearing surface, small pockets or pads are machined to create areas of high pressure fed by these restrictors and from which the oil flows ,to the rest of the bearing surfaces before exiting the bearing. The oil is then collected, filtered, repressurized, and recirculated. [Handbook, pg. 294]
ANANT JAIN
Hydrostatic Slide
Introduction:
A Hydrostatic slide is non-contact in that the slide is supported by a film of high pressure oil, in the order of 10 Um. It functions by producing a continuous flow of high pressure oil through and out of the bearing. The flow rate being controlled by restrictors. The restrictors allow the slideway to cope with varying loads and maintain a near constant film thickness. Throughout the bearing surface, small pockets or pads are machined to create areas of high pressure fed by these restrictors and from which the oil flows ,to the rest of the bearing surfaces before exiting the bearing. The oil is then collected, filtered, repressurized, and recirculated. [Handbook, pg. 294]
At a fundamental level, in hydrostatic slide there is no mechanical contact due to which it offers several advantages over roller bearings:
-
As the entire mass is supported on a thin fluid film, the static and dynamic friction is extremely low. A mass supported on a hydrostatic slide will silently glide down the smallest inclination
-
Due to low friction, hydrostatic slides can achieve high speed and accelerations which is a desirable feature for high speed machining and applications requiring rapid oscillations such as camshaft grinding
-
As there is no metal-to-metal contact hydrostatic slides and (theoretically) zero wear the machine bearing life is virtually infinite [Rowe, 11]
-
In a hydrostatic slide the moving element is buffered from surface contacts in all directions, which helps in vibration damping, an important criterion for achieving surface texture
-
Hydrostatic slides offer excellent load carrying capacity as compared to aerostatic bearings
Advantages of Hydrostatic Slide:
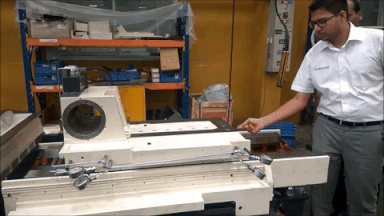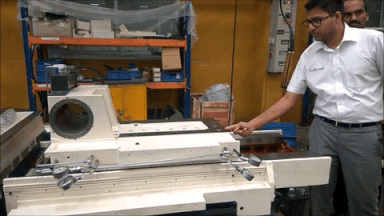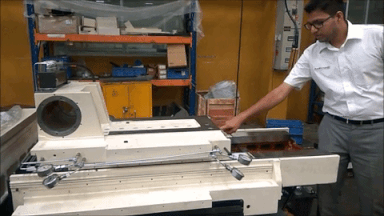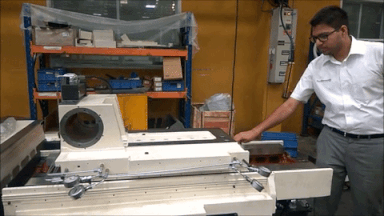
Hydrostatic slide at MGT: Friction is so low that ta 350 Kg Slide can move with the force of one finger
Through the above advantages the machine tool industry has made extensive use of hydrostatic bearings, where they have proved to be reliable and predictable and have often improved the performance of the machine beyond the capability of any other bearing.[Rowe, pg. 8]
Need
One of the immediate requirements for hydrostatic slide in MGT was for non-round grinding, which involves grinding of non-circular contours on a cylindrical grinding machine through the interpolation of wheel in-feed (X-axis) and work-piece rotation (C-axis). Although MGT had successfully supplied this machine in 2014 with roller element slides; high productivity segments such as cam-lobe grinding require low-friction slides for rapid oscillations to achieve faster cycle times.
2.5 x faster machine response with low friction hydrostatic slide
Non-Round Grinding on an MGT machine with conventional roller bearing guideways
Non-Round Grinding on an MGT machine with Hydrostatic slide for in-feed
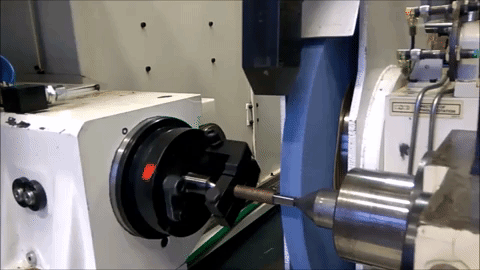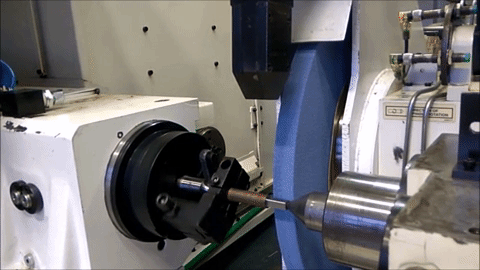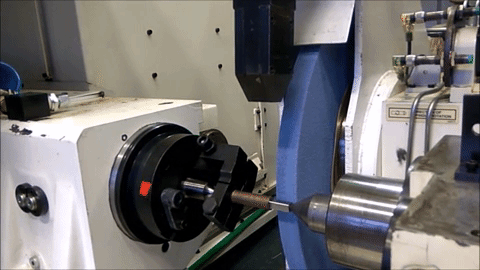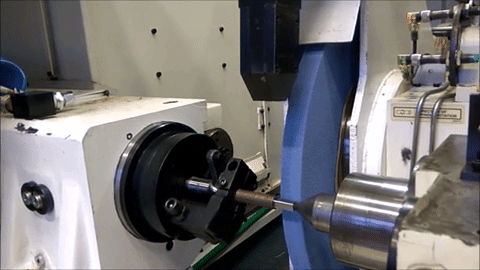
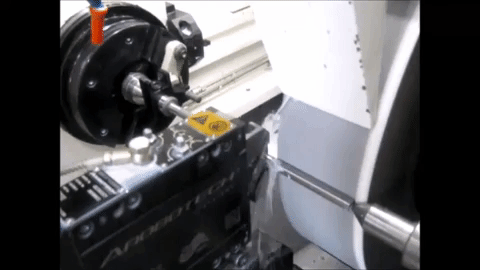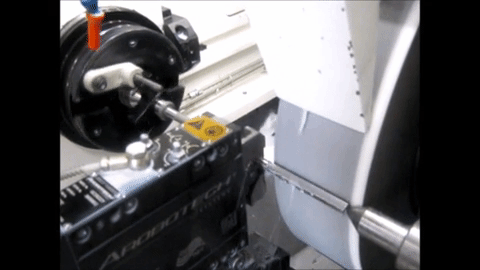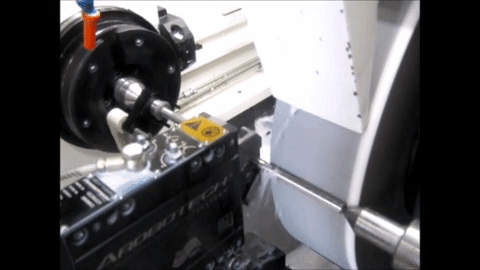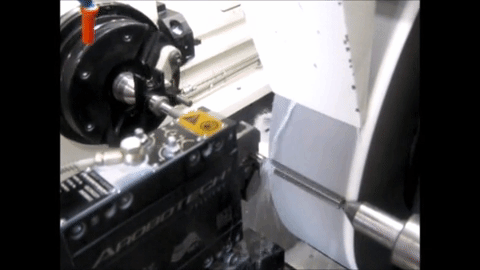
Project Definition and Organization
The project was initiated with the intention of implementation on machines developed for Cam-lobe Grinding process and M2G (Machining to Grinding) process.
The project consisted of the following modules:
-
Technology Research which involved:
-
Basic Science of Hydrostatic Bearings
-
Advantages and application in machine tools
-
Requirement for MGT
-
Different flow control techniques and those being commercially used
-
-
Identification of design and characteristic parameters:

e project consisted of the following modules
3. Benchmarking: of above mentioned parameters through case studies of commercial hydrostatic units [Ref: W2]
4. Mathematical Modelling: The Mathematical Modelling has been divided into two modules:
-
Single Pocket Calculations: This includes the mathematical modelling to relate the effect of design parameters such as pocket dimensions on the characteristic parameters mentioned in figure above.
Single Pocket Calculation to calculate the pressure distribution in a hydrostatic pocket
Meshing across a hydrostatic pocket to compute the pressure distribution by solving Reynold’s equation using a finite difference approach

Pressure Distribution calculated by the mathematical model

Bode Plot, calculated through the mathematical model indicates the dynamic stiffness characteristics of the a single hydrostatic pocket
-
Dynamic Force Analysis for a multi-pocket slide: The Hydrostatic slide on a grinding machine has more than one pocket to support the slide against various forces and moments as can be seen in the tale below:

It is vital that the hydrostatic pockets can support all the external forces and moments in all the 18 scenarios mentioned in the table and provide the desired output characteristics.
All these 18 scenarios have been formulated as a constrained multi-body dynamics model wherein:
-
The Hydrostatic forces have been formulated as a non-linear springs
-
The Hydrostatic slide has been assumed as a rigid body [ref Slocum] with all the pocket heights defined as a function of the Centre of Gravity's linear displacements and euler rotations (CG Configuration) [Ref Krendall]
-
Non-Linear optimization has been used to arrive at the optimum CG configuration and hence the hydrostatic pocket heights and forces which can support the slide against external loads
Major Areas of Learning
-
Hydrostatic Systems:
-
Working and Science
-
Configurations of commonly used Hydrostatic Restrictors
-
-
Numerical discretization and finite difference approach for solving differential equations
-
Vibration Modelling for a Hydrostatic pocket
-
Rigid Body Dynamics:
-
Computational Methods in Kinematics
-
Constrained Dynamics
-
Euler Angles and Rotations
-
-
Non-Linear Optimization
-
Hydraulic elements in a machine tool
Accomplishments:
-
Algorithm Development for Design of Hydrostatic Slideways:
-
Inputs:
-
Magnitude and location of external forces
-
Slide configuration [Pocket Dimensions and locations]
-
Oil Viscosity
-
-
Algorithm Outputs:
-
Suitability of the Hydrostatic system to for the machine configuration and external forces
-
Characteristics such as load carrying capacity, oil flow, stiffness, temperature increase
-
-
-
Hydrostatic Slide successfully designed, fabricated and assembled on a grinding machine
-
This work has resulted in commercial impact to the company through the sales of non-round grinding machine
Hydrostatic Slide, assembled on grinding machine moves with the force of 1 finger